Measuring Design Maturity – Creating Aha! Moments
Is your product development team struggling to create exceptional user experiences; which we refer to as Aha! Moments? This frustrating scenario is all too common for business leaders, and the root cause may lie in your organization's level of design maturity.
The concept of Design (UX) maturity was first introduced by UX expert Jakob Nielsen in 2008 in response to the growing need for organizations to understand and improve their user experience practices. Nielsen recognized that companies were at different stages of UX sophistication, directly impacting their ability to create user-centric products.
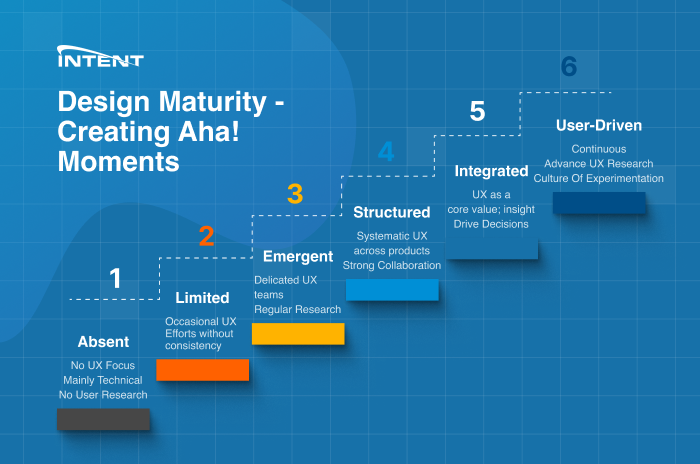
Over the past 25 years, the UX landscape has evolved significantly. The early concepts have evolved resulting in a more comprehensive and up-to-date model. The six-level UX Maturity Model has become a popular way of assessing and advancing UX capabilities within software organizations.
Understanding the UX Maturity Model
The UX Maturity Model is a comprehensive framework designed to help software organizations assess their current level of user experience proficiency and identify areas for improvement. By providing a clear roadmap for UX growth, this model enables companies to make strategic decisions that enhance their product development processes and ultimately lead to better user experiences.
The model consists of six stages, each representing a different level of UX sophistication and integration within an organization. As companies progress through these stages, they gradually develop a deeper understanding of user needs, implement more effective UX practices, and create products that truly resonate with their target audience.
Stage 1: Absent
At the lowest level of UX maturity, organizations are either unaware of the importance of user experience or actively choose to ignore it. UX is not considered a priority in these companies, and little to no effort is made to understand or address user needs.
Characteristics:
- Lack of dedicated UX teams or resources
- Focus product development solely on technical functionality
- Conduct no user research or employ user-centered design processes
- Base decisions on assumptions rather than user insights
The consequences of ignoring UX can be severe, with far-reaching implications for a company's success. Products created by organizations at this stage often suffer from poor usability, high user frustration, and low adoption rates.
For example, a software company that fails to consider user needs may develop a product with a steep learning curve, leading to high abandonment rates and negative word-of-mouth. As users share their bad experiences, the company's reputation can suffer, making it harder to attract and retain new customers.
Moreover, ignoring UX doesn't just hurt sales and reputation in the short term; it can also hinder a company's ability to innovate and adapt to changing user preferences. When organizations don't value user feedback, they miss out on crucial insights that could help them improve their products and stay ahead of the competition.
Over time, products that fail to evolve and meet user needs will fall behind, especially compared to competitors who prioritize UX from the start and continuously iterate based on user input.
Stage 2: Limited
Organizations at the limited stage of UX maturity have begun to recognize the importance of user experience, but their efforts are often sporadic and inconsistent. Individual teams or departments may undertake UX initiatives, but no company-wide strategy or commitment to user-centered design exists.
Characteristics:
- Conduct sporadic UX activities, like usability testing and user interviews
- Apply UX best practices inconsistently across products
- Allocate scarce UX resources and budgets
- View UX as an optional enhancement, not essential to product development
Organizations facing limited UX maturity encounter various challenges that impede their progress. They often struggle to demonstrate the value of UX to stakeholders, who may not immediately see its impact on the bottom line. This struggle is compounded by inconsistent user experiences across products and touchpoints, highlighting a lack of uniformity and coherence in their UX efforts.
Furthermore, these organizations typically have limited UX skills and knowledge. This makes it challenging to adopt and implement effective UX practices. Resistance to change is another significant hurdle, particularly from teams accustomed to traditional development processes that may not prioritize user needs.
Stage 3: Emergent
At the emergent stage of UX maturity, organizations have begun to embrace user experience as a critical component of their product development process. UX teams are established, and user-centered design practices are more consistently applied.
Characteristics:
- Have dedicated UX teams with strong leadership support
- Conduct regular user research, including interviews, surveys, and testing
- Promote collaboration between UX and development teams across the product lifecycle
- Increase organizational awareness of UX best practices and principles
While organizations at the emergent stage have made significant progress in their UX maturity, they still face several challenges. One of the primary issues is the inconsistent application of UX processes across different teams. This lack of uniformity can lead to varying levels of user experience quality and make maintaining a cohesive product strategy difficult. Additionally, user insights may not be fully integrated into strategic decision-making, resulting in missed opportunities to align product development with user needs and preferences.
Another challenge emergent organizations face is measuring the impact of UX on business outcomes. Without clear metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs), it can be difficult to demonstrate the value of UX investments to stakeholders and secure ongoing support and resources. Furthermore, some stakeholders may not fully appreciate the value of UX, leading to resistance or pushback when allocating time and budget to user research and design activities.
Stage 4: Structured
As organizations progress to the structured stage of UX maturity, they implement systematic UX methodologies deeply integrated into their product development processes. UX teams are well-established and have a clear mandate to guide the organization toward user-centered design.
Characteristics:
- Employ robust UX processes consistently
- Conduct extensive user research throughout the product lifecycle
- Align UX objectives with overall business goals and strategies
Foster strong collaboration between UX, development, and other key stakeholders.
Implementing a structured UX approach brings numerous benefits to organizations. It ensures that user needs and preferences are consistently considered and addressed throughout product development. This leads to higher-quality products that are more likely to satisfy users. Moreover, a structured approach helps optimize resource allocation and reduces the risk of costly design missteps.
However, there are also limitations to consider. Rigidly adhering to UX processes may sometimes stifle creativity and innovation. Organizations must balance structure and flexibility to allow experimentation and adaptation to changing user needs. Additionally, the success of a structured approach relies heavily on the skills and expertise of the UX team, so ongoing training and professional development are crucial.
Stage 5: Integrated
At the integrated stage, UX is no longer a separate function but deeply embedded in the organization's DNA. User-centered thinking permeates every aspect of the company, from strategy and decision-making to product development and customer support.
Characteristics:
- Embrace UX as a core value and competitive differentiator
- Integrate UX insights into all strategic and operational decisions
- Foster a user-centric culture that empowers all employees
- Continuously measure and optimize UX to drive tangible outcomes
Organizations at this stage reap the benefits of a genuinely user-centric approach. By placing the user at the heart of everything they do, they can create products that exceed user expectations. This leads to increased customer loyalty, higher conversion rates, and sustainable business growth.
Cultivating a user-centric culture across all levels of the organization is vital to achieving and maintaining UX maturity. This requires ongoing education, communication, and reinforcement of UX principles and best practices. Leaders must actively champion UX and ensure it remains a top priority despite competing demands and pressures.
Stage 6: User-Driven
At the pinnacle of UX maturity, organizations are user-driven, meaning that deep user insights and a relentless focus on user needs drive all aspects of the business. UX is not just a priority but is the guiding force behind every decision and action.
Characteristics:
- Conduct continuous, in-depth user research to uncover latent needs and opportunities
- Employ advanced UX methods, such as predictive analytics and machine learning
- Rapidly prototype and test new ideas to validate user value before full-scale development
- Foster a culture of experimentation, learning, and iteration based on user feedback
Achieving UX excellence through deep user insights provides organizations with a significant competitive advantage. By truly understanding and anticipating user needs, they can create innovative products and experiences that set them apart from rivals. This helps them attract and retain customers and positions them as industry leaders and trendsetters.
However, reaching and sustaining this level of UX maturity can be challenging. It requires a significant and ongoing investment in UX research, talent, and resources. Organizations must be willing to challenge the status quo and take calculated risks based on user insights, even if it means diverging from industry norms or conventional wisdom.
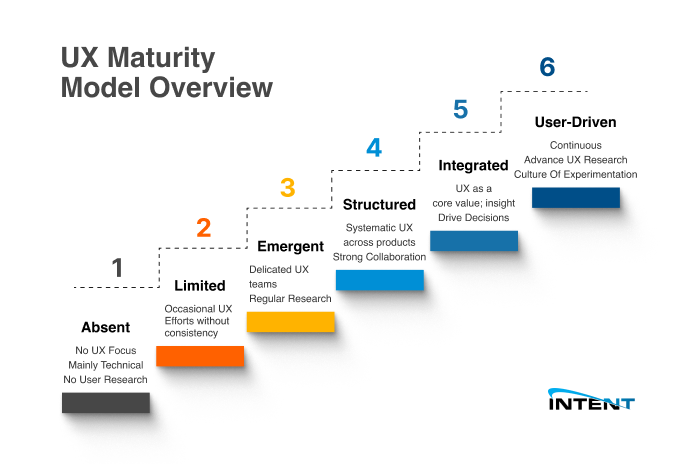
UX Maturity Model Overview
To help you navigate the UX journey easily, here’s a summary of the six stages of UX maturity, highlighting key characteristics and challenges/outcomes for each stage.
Stage | Characteristics | Challenges and Outcomes |
1. Absent | No UX focus; mainly technical; no user research. | Products hard to use; unsatisfying user experience. |
2. Limited | Occasional UX efforts without consistency. | Struggle to prove UX's value; uneven user experiences. |
3. Emergent | Dedicated UX teams; regular research. | Inconsistent UX processes; difficulty using user insights. |
4. Structured | Systematic UX across products; strong collaboration. | Balancing creativity with structure is challenging. |
5. Integrated | UX as a core value; insights drive decisions. | Embedding a user-centric culture is challenging. |
6. User-Driven | Continuous, advanced UX research; culture of experimentation. | Requires significant investment in UX resources. |
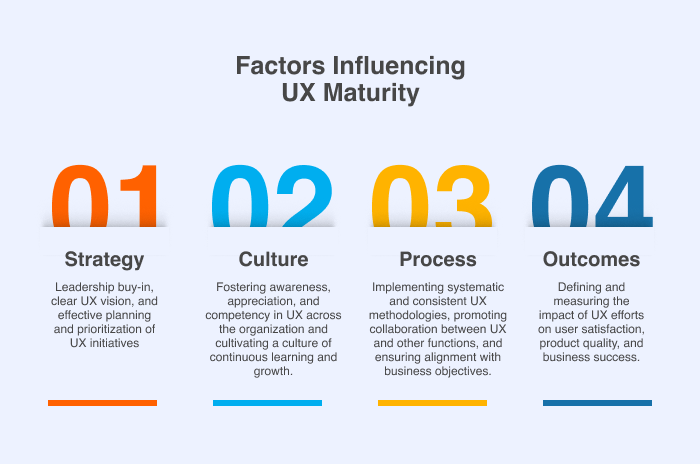
Factors Influencing UX Maturity
Several key factors contribute to an organization's UX maturity, including:
- Strategy: Leadership buy-in, clear UX vision, and effective planning and prioritization of UX initiatives
- Culture: Fostering awareness, appreciation, and competency in UX across the organization and cultivating a culture of continuous learning and growth.
- Process: Implementing systematic and consistent UX methodologies, promoting collaboration between UX and other functions, and ensuring alignment with business objectives.
- Outcomes: Defining and measuring the impact of UX efforts on user satisfaction, product quality, and business success.
By assessing these factors, organizations can identify strengths and weaknesses in their current UX practices and develop targeted strategies for improvement.
How To Assess Your Organization's UX Maturity
To determine where your organization stands regarding UX maturity, conducting a comprehensive audit is essential. This process involves evaluating current UX practices, analyzing processes and deliverables, and gathering insights from team members across the organization. By identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, you can create a roadmap for advancing your UX maturity.
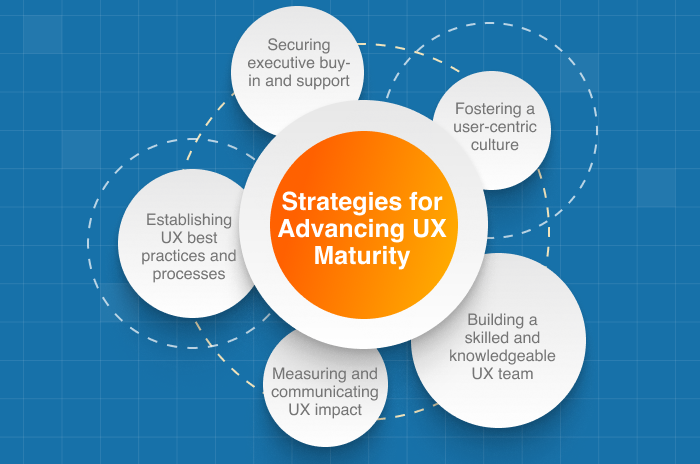
Strategies for Advancing UX Maturity
Progressing through the stages of UX maturity requires a strategic and sustained effort. Key strategies for advancing UX maturity include:
- Securing executive buy-in and support: Engage leadership by demonstrating the business value of UX and aligning UX initiatives with organizational goals.
- Building a skilled and knowledgeable UX team: Invest in hiring, training, and professional development to ensure your UX team possesses the necessary expertise and skills.
- Establishing UX best practices and processes: Develop and implement standardized UX methodologies, tools, and workflows to ensure consistency and effectiveness.
- Fostering a user-centric culture: Promote awareness and understanding of UX principles throughout the organization, and encourage cross-functional collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Measuring and communicating UX impact: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) for UX success, and regularly report on the outcomes and value delivered by UX efforts.
While advancing UX maturity is a gradual process, the rewards are significant. By investing in UX and striving for higher maturity levels, software organizations can deliver exceptional user experiences, drive customer loyalty, and achieve sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive market.
Elevate Your UX Maturity
At Intent SG, we recognize that every organization's UX maturity journey is unique, with its own challenges and opportunities. As a software development company specializing in helping organizations enhance their engineering teams and deliver high-quality products, we take a customized approach to supporting our clients' UX maturity efforts.
Our team of experienced UX professionals offers a range of services designed to help organizations assess their current state of UX maturity, identify areas for improvement, and implement proven strategies and best practices to drive progress.
Here are some ways we can support your organization's UX maturity journey:
- Assess your current UX maturity level and provide actionable recommendations
- Define and implement a UX vision and roadmap aligned with your business objectives
- Offer training and education programs to build UX skills across your organization
- Embed UX professionals within your teams for hands-on support and guidance
- Develop custom tools and frameworks to streamline your UX processes
- Provide ongoing coaching and mentoring to help your UX team grow and develop
We believe advancing UX maturity means fundamentally shifting how your organization thinks about and approaches user experience. Our team is passionate about UX and dedicated to helping our clients succeed, and we look forward to the opportunity to support you in driving your organization's UX maturity forward.




